Graph 1. Productivity by career.
doi.org/10.15178/va.2021.154.e1199
RESEARCH
METRIC ANALYSIS OF THE SCIENTIFIC PRODUCTION ABOUT THE RADIO IN THE DIPLOMA WORKS OF THE PERIOD 2013-2018
ANÁLISIS MÉTRICO DE LA PRODUCCIÓN CIENTÍFICA SOBRE LA RADIO EN LOS TRABAJOS DE DIPLOMA DEL PERÍODO 2013-2018
ANÁLISE MÉTRICA DA PRODUÇÃO CIENTÍFICA SOBRE A RÁDIO NOS TRABALHOS DE GRADUAÇÃO NO PERÍODO 2013-2018
Beatriz Elena Fonseca Muñoz
Reinaldo Joel Martínez de Armas1
1University of Havana. Cuba.
[1] Beatriz Elena Fonseca Muñoz: Doctora en Ciencias de la Comunicación, profesora de Comunicación sonora, Jefa de la disciplina Comunicación y lenguajes mediáticos, asesora de dramas radiales.
ABSTRACT
The present article exposes the results of the metric analysis applied to the scientific production of the works of diploma on the radio, in the careers of Social Communication and Journalism, respectively, that between 2013-2018 were realized in the Faculty of Communication of the University of Havana. Some theoretical aspects are exposed on the concept of diploma work that governs higher education in Cuba, in relation to the situation of radio research, as well as historical elements on the development of bibliometric studies. One-dimensional and multidimensional bibliometric indicators are used. The first ones include productivity by career, by years, by tutors and by keywords, and among the latter, the co-occurrence of keywords and collaboration in tutoring. The tools used in the data processing are concentrated in the bibliographic manager EndNote X7, Microsoft Excel 2013, Bibexcel version 2016 and Gephi 0.9.2. The measurement shows that the radio has a very discreet increase as a center of interest in the research of the Faculty. It is necessary to draw up strategies that broaden its presence in the field of research and deepen its knowledge, taking into consideration that as a means of communication it still coexists with others despite the transformations that society experiences in information and communication technologies and to which it adapts.
KEY WORDS: Radio, Metric studies, Communication research, Interdisciplinary, Scientific production, Social Communication, Journalism.
RESUMEN
El presente artículo expone los resultados del análisis métrico aplicado a la producción científica de los trabajos de diploma sobre la radio, en las carreras de Comunicación Social y Periodismo, respectivamente, que entre 2013-2018 se realizaron en la Facultad de Comunicación de la Universidad de La Habana. Se exponen algunos aspectos teóricos sobre el concepto de trabajo de diploma que rige la educación superior en Cuba, en relación con la situación de la investigación en la radio, así como elementos históricos sobre el desarrollo de los estudios bibliométricos. Son utilizados indicadores bibliométricos unidimensionales y multidimensionales. Entre los primeros se encuentran la productividad por carrera, por años, por tutores y por palabras clave y entre los segundos, la coocurrencia de palabras clave y la colaboración en tutoría. Las herramientas empleadas en el procesamiento de los datos se concentran en el Gestor bibliográfico EndNote X7, Microsoft Excel 2013, Bibexcel versión 2016 y Gephi 0.9.2. La medición realizada muestra que la radio tiene un incremento muy discreto como centro de interés en las investigaciones de la Facultad. Es preciso trazar estrategias que amplíen su presencia en el campo investigativo y profundicen en su conocimiento, tomando en consideración que como medio de comunicación aún coexiste con otros a pesar de las transformaciones que la sociedad experimenta en las tecnologías de la información y la comunicación y a las que se adapta.
PALABRAS CLAVE: Radio, Estudios métricos, Investigación en comunicación, Interdisciplinar, Producción científica, Comunicación Social, Periodismo.
RESUMO
O presente artigo mostra os resultados da análise métrica aplicada à produção científica dos trabalhos de graduação sobre a rádio, nas graduações de Comunicação Social e jornalismo, respectivamente, que entre os anos 2013-2018 se fizeram na Faculdade de Comunicação da Universidade de La Habana. Se mostram alguns aspectos teóricos sobre o conceito de trabalho de graduação que define a educação superior em Cuba, em relação com a situação da pesquisa sobre rádio, assim como elementos históricos sobre o desenvolvimento dos estudos bibliométricos. São utilizados indicadores bibliométricos unidimensionais e multidimensionais. Entre os primeiros estão a produtividade por graduação, por anos, por professores e por palavras chave e entre os segundos, a ocorrência de palavras chave e a colaboração em tutoría. As ferramentas usadas no processamento dos dados se concentram no Gestor bibliográfico EndNote X7, Microsoft Excel 2013, Bibexcel versão 2016 e Gephi 0.9.2. A medição realizada mostra que a rádio tem um incremento muito discreto como centro de interesse nas pesquisas da Faculdade. É preciso criar estratégias que expandam sua presença no campo investigativo e aprofundem o seu conhecimento, levando em consideração que como meio de comunicação ainda coexiste com outros, mesmo quando a sociedade experimenta mudanças nas tecnologias da informação e comunicação a que se adapta.
PALAVRAS CHAVE: rádio, estudos métricos, pesquisa em comunicação-interdisciplinar, produção científica, Comunicação Social, Jornalismo.
Correspondence:
Beatriz Elena Fonseca Muñoz. University of Havana. Cuba. beatrizelena@fcom.uh.cu
Reinaldo Joel Martínez de Armas. University of Havana. Cuba. joel@fcom.uh.cu
Received: 27/05/2020.
Accepted: 16/12/2020.
Published: 12/03/2021.
How to cite this article:
Fonseca Muñoz, B. E. y Martínez de Armas, R. J. (2021). Análisis métrico de la producción científica sobre la radio en los trabajos de diploma del período 2013-2018. Vivat Academia. Revista de Comunicación, 154, 69-84. http://doi.org/10.15178/va.2021.154.e1199
http://www.vivatacademia.net/index.php/vivat/article/view/1199
Translation by Paula González (Universidad Católica Andrés Bello, Venezuela).
1. INTRODUCTION
Metric studies are one of the methods that make it possible to offer another look at the behavior of the radio field as an object of research. When applied in the space of information and scientific knowledge, bibliometrics is a tool that allows revealing some of the various processes and phenomena that occur in different areas, as well as the trends that are externalized in them, such as: production, productivity, authorship, and collaboration that are manifested in the development of research, through the study of its reports. In this article, they refer to the diploma works of completion of studies in the careers of Social Communication and Journalism, respectively.
In the higher education system in Cuban society, diploma work is understood as the “type of research work that students can carry out and that allows them to acquire a greater mastery and update of the scientific methods and techniques characteristic of the profession. It is done individually and, generally, in one of the professional's spheres of action” (Regulation, 2018, p. 690).
In the Regulation of teaching and methodological work of higher education, it is stated that the diploma works should contribute to the development of initiative, independence, and creativity of students. It should also strengthen individual work and encourage interdisciplinary analysis in solving the problem that is formulated as an object of research.
These works are directed by the professors, according to their preparation in the various topics, to match their skills with the objectives and complexity of the topic that each student assumes in their research work. The specialists who work in the different labor entities, teaching units, research centers, and who enjoy recognition, can participate in this direction through joint work with teachers.
The diploma work is evaluated through its defense, which aims to verify the mastery of the students of the general objectives of the career, by independently solving a problem of the profession. They use the methodology of scientific research for this.
Radio has been one of the research objects of these diploma works. By identifying the topics of interest on which they focus, the following stand out: the construction of gender in the radio scene, the soundscape of the Cuban capital, the realization of radio reports and documentary radio, the analysis of the main features of the process of reception of musical radio programs by young people from the capital, foundation and design of a university web radio, the characterization of the production process of a radio program, life stories of radio personalities, and the construction of professional portfolios.
The production of various ways of doing radio (musical, informative, and dramatized programs) is one of the lines of research with the greatest presence, expanding the vision of the medium as an organization that manages communication in various spaces and by different actors.
The consumption of radio dramas in a province in the eastern part of the country constitutes a milestone in the research field of the faculty, since this type of study in the medium has no antecedents, not even in the production company where they are created.
The design of a university web radio indicates the views towards radio in the context of information and communication technologies, which is why the work of the media is enriched by expanding its use in new spaces and content.
These results could give the idea that radio as a medium widely monopolizes research; however, this is not exactly the case.
In a study carried out for the Ibero-American area, Piñeiro- Otero and Martín- Pena (2018), highlight that:
Radio is a highly relevant medium in Latin America, although its study has not been reflected in the same way in academia. Regardless of the differences between contexts, radio constitutes a minority line, even in those topics with the greatest projection in Ibero-American communication research. For researchers, radio has hardly been of interest to the academy, profession, or public powers, which has fed back its status in communication research. (p.105)
A situation that is not very different in the Cuban context, specifically, in the context of the Faculty of Communication of the University of Havana, a teaching and research center, in which the study presented here is located.
The diploma works analyzed, also called “gray literature” (Puente en Hernández, 2016), have as object of study different dimensions or aspects that characterize radio as a means of communication and some of which are mentioned previously.
Among the research methods and techniques that were used in the works of the sample are: documentary and bibliographic analysis, in-depth interviews, content analysis, surveys, and discourse analysis, showing the variety of tools used to develop research.
The use of metric studies to specify the behavior of scientific production related to radio research marks the interdisciplinary perspective that is applied to the study, if it is understood as the “transfer of methods from one discipline to another” (Nicolescu, 1999, p. 35), making them common tools. Metric studies are proof of this when applied to the discovery of some of the specificities that characterize studies about radio.
The radio medium is a "theoretical fact", that is to say, it is susceptible to being analyzed from different points of view to broaden the views on this means of communication and base the processes that occur in said medium. The application of bibliometrics in its study enables an analysis different from those traditionally directed towards radio.
The year 1896 marks the initial reference on Information Metric Studies (IMS). It is Campbell who indicates the scoop by focusing his analysis by topic.
The publication of different works in Science Progress under the title of Statistical Analysis of Literature, in 1917, whose authors were Cole and Eales, exposes the scientific production on comparative anatomy between the years 1550 and 1860, its distribution by countries, and the division by animal kingdom. Statistical analyzes are accompanied by graphic representations to improve them.
Another aspect that stands out in the development of this type of study is the frequency of contribution of the authors. Lotka, in 1926, published his article on the matter and explained a bibliometric quantification law that shows the distribution of authors according to their productivity and which will be known as Lotka's Law.
The articles published in 1926 in journals on Chemistry and indexed in The Journal of American Society, constitute the bases of the analysis that Gross and Gross carried out in 1927 on the bibliographic references of said articles, thus setting what would later be called citation analysis.
Together with this law, others are known, such as Zipf's Law and Bradford's Law. The first, created in 1940 by George Kingsley Zipf, who studied different languages applying statistical analysis and focuses on the frequency with which words are used in the text.
The second was proposed by Samuel Bradford in 1948 and refers to the dispersion of the scientific literature, becoming an important methodological aspect to formulate the indicator on impact factor, by the Science Citation Index, specifically by Eugene Garfield and Irving H. Sher, in 1963.
The interdisciplinary nature of metric studies is indicated, generally, from various mathematical and statistical models and methods and with the disciplines that make up the Informational Bibliological Knowledge System. This character is highlighted here based on the possibility of applying mathematical methods and models to analyze trends (Gorbea en García, 2005) in the field of radio.
2. OBJECTIVES
The objective of the study was to analyze the behavior of scientific production about radio in the diploma works of the degrees of Journalism and Social Communication, respectively, in the period 2013-2018, and this article, for its part, to present these results. For this, theoretical aspects that contextualize the research object are explained from the understanding of what a diploma work consists of, some considerations related to the situation of research on radio, and historical elements concerning the development of bibliometric studies.
A mixed methodology is applied, since qualitative assessments that characterize the trends analyzed are inferred from quantitative data.
3. METHODOLOGY
The documentary collection of the diploma thesis of the Journalism and Social Communication careers was reviewed, to find the theses that addressed radio as a central theme between 2013 and 2018, finding 43 theses. These were registered in a bibliographic database made up of the following fields: author, defense year, title, tutor (s), academic department, and keywords. The records contained in the database formed the data set to perform the metric study.
One-dimensional and multidimensional bibliometric indicators were used:
One-dimensional indicators:
Multidimensional indicators:
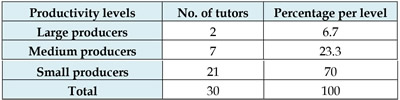
In the case of the analysis of the productivity indicator by tutors, the distribution is adopted according to the levels proposed by Lotka: Large producers 10 or more works, Medium producers from 2 to 9 works, and Small producers 1 work.
Tools:
The tools used in the data processing were the following: EndNote X7 bibliographic manager, Microsoft Excel 2013, Bibexcel version 2016, and Gephi 0.9.2.
The EndNote bibliographic manager was used to create the database containing the records of the theses and to elaborate the frequency indexes of the indicators.
Microsoft Excel was used to prepare the graphs and tables.
With Bibexcel, the co-occurrence lists and net domain files were created.
The Gephi was used to visualize and analyze collaborative networks and word clouds.
4. DISCUSSION
4.1. Productivity by career
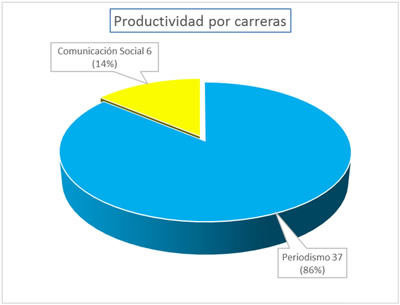
Radio as a research topic was treated in 43 diploma theses between 2013 and 2018. As can be seen in
Graph 1, the Journalism career was the most productive with 37 works, representing 86% of the total. Meanwhile, in the Social Communication career, only 6 theses were carried out, representing 14% of the total.
It is considered that the highest level of concentration of productivity is found in Journalism as it is the space with the greatest visibility of the profession in the media and, in this case, the radio.
Understanding the functions of the communicator in the media is a gradual process that does not yet manifest a conscious assumption, sometimes by decision-makers who must, for example, place recent graduates in media spaces and by the organizations that receive these graduates who are starting their working life.
Although the curricula have been updated and broadened and deepened in the functions that a communicator must fulfill, it is necessary to understand the different roles that a social communicator can assume in the media and that it is not reduced to the production process, but rather it extends to strategic work within the media organization. The clearer the vision of the functions that the social communicator can perform in the media field, to that extent the edges that are objects of research in the medium will be more diverse to support those functions.
Source: self-made.

Graph 1. Productivity by career.
4.2. Productivity by years
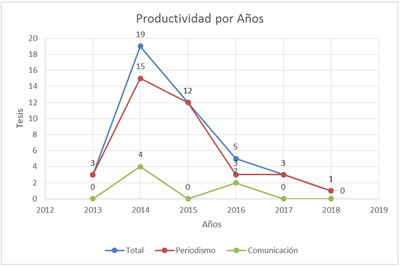
Graph 2 shows the behavior of thesis productivity by years. 2014 was the year where productivity reached its highest value, from this it can be inferred that this was due to the interest that the portfolio modality aroused as a culmination of studies, which allows students to remain during a course in the media observing their production process, better understand their ways of making and creating materials. The work practice also links them to the media, but only for a month, which does not allow a closer relationship with this space that is attractive to students.
Since 2015 there is a continuous decrease in the amount of research on radio, with 2018 being the least productive year with only 1 thesis. The analysis by careers gave as a result that in Journalism, radio was researched in each of the years analyzed, in contrast, in the Social Communication career it was only researched in the years 2014, 2016, and 2018.
Source: self-made.
Graph 2. Productivity by years.
4.3. Productivity by tutors
The analysis of the most productive tutors was carried out from the 30 teaching or radio media tutors declared in the diploma theses. As can be seen in Table 1, the distribution of tutors, according to their level of productivity, was as follows: 2 were located at the level of large producers, 7 as medium producers, and 21 as small producers.
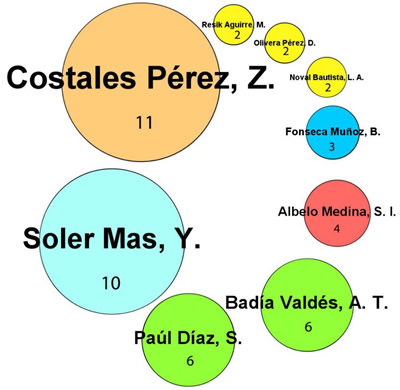
The Ph.Ds. in Science and professors of the Faculty of Communication Zenaida Costales Pérez and Yanela Soler Más were the most productive with 11 and 10 theses respectively, for which they were located at the levels of large producers, as can be seen in Graph 3. The first, a Journalism graduate, has more than 30 years of experience in radio news programming, is a professor at the Faculty of Communication, and its Vice-Dean for Research and Postgraduate Studies. The second also graduated from Journalism and has work experience in radio.
It corresponds to the highest number of works in Journalism that is reflected in the analysis of productivity by career.
Table 1. Productivity levels by tutors according to Lotka.
Source: self-made.
Source: self-made.
Graph 3. Productivity by tutors at the large and medium levels of producers.
4.4. Tutoring collaboration
The collaboration between tutors, co-tutors, and consultants is given by the relationships that are established between teachers of the Faculty of Communication and professionals of the radio medium for the advice of students who carry out diploma works.
The Tutoring Collaboration network (Graph 4) is made up of 48 nodes and 58 edges, which is why it is considered small. 7 clusters of different colors are distinguished. Its density is low (0.026), which indicates the presence in the network of disconnection and fragmentation in small groups, as can be seen in the disconnected clusters with the colors yellow, red, pastel blue, and light brown. Furthermore, cohesion is low, with strong centralization and inequality among the actors prevailing.
The nodal degree represents the number of links or bonds of a given node; and intermediation measures the frequency with which a node appears in the shortest path connecting two other nodes in a network. In the graph, Zenaida Costales Pérez stands out as it has 14 links and is the one with the highest nodal degree, besides, it is the one with the highest frequency of intermediation with 111.5. Next is Yanela Soler Más with a nodal degree of 11 and an intermediation frequency of 63.5. This indicates that both professors from the Faculty of Communication have a greater presence in tutoring on the topic of Radio, both in collaboration with other professors from the faculty and with media professionals linked to them.
These two professors belong to the Department of Journalism and their topics correspond to this profile, therefore, it is consistent with what is indicated above about the fact that it is in this career where the greatest number of diploma works are found.
Dr. Zenaida Costales in the role of tutor is linked to the following professors and media professionals: B.S. Norka Meisozo Reyes, B.S. Carlos Luis Molina, Dr. Yanela Soler Más, Dr. Isabel Moya Richard, B.S. Kathy Rojas Pérez, B.S. Sonia Rodríguez Alemañy, Dr. Silvia Ivonne Albelo Medina (twice), B.S. Alina Sánchez del Collado, B.S. Ibet García Álvarez, B.S. Nelson Rodríguez Crespo, B.S. Magaly Lahera Valdés, B.S. Max Barbosa Miranda, Dr.C. Ana Teresa Badía Valdés. And Dr. Yanela Soler Más is related to: MsC. Francisco Delgado Márquez, MsC. Magda Resik Aguirre, B.S. Angélica Paredes López, Dr. Iraida María Calzadilla Rodríguez, B.S. Olivia Terry, B.S. Pedro Manuel Otero Cabañas, B.S. Yerisleydys Menéndez García, B.S. Liliana Soto Llorca, B.S. José Raúl Belén Acosta (twice), B.S. Mireya Santana González, Dr. Zenaida Costales Pérez.
Source: self-made.

Graph 4. Tutoring collaboration.
4.5. Productivity by keywords
Productivity by keywords allows us to know the aspects most covered within the radio theme in the period 2013 - 2018. In this research, the keywords assigned by the authors of the diploma works are used.
In the analysis carried out, a total of 112 keywords were identified, the most assigned being radio and journalism on a total of 9 occasions. This was an expected result since the radio is the main subject that is analyzed and in Journalism was where it was researched the most. Next in the ranking of keywords are: Radio Rebelde, communication products, and productive routines with 5 assignations.
This situation could be taken as an indicator of what was previously indicated regarding the visibility and understanding of the functions that the journalist and the social communicator can and should perform, respectively.
Source: self-made.
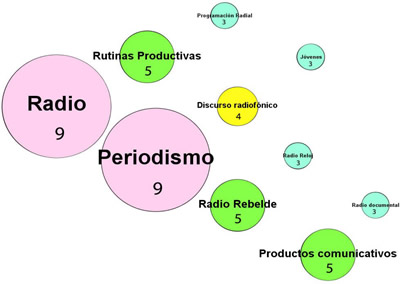
Graph 5. Productivity by keywords.
4.6. Keyword co-occurrence
Graph 6 represents the keyword co-occurrence network, composed of 109 nodes and 245 edges, which is why it is considered a medium-sized network. 14 clusters of different colors are displayed. The density of the network is low (0.021) and 7 disconnected clusters are observed with the colors orange, light pastel blue, white, light brown, light green, pink, and light gray. The cohesion is low prevailing a strong centralization.
The keyword radio presents the highest nodal degree with 27 links followed by journalism with 18, and radio speech 16. The highest frequency of intermediation was for journalism with 355, followed by radio 243, and communication products 168.5.
These results confirm that radio has its centrality in the Journalism career because of the consolidation of the specialty in the medium and the study of its way of doing, hence the radio discourse also has one of the largest presences in the network of keyword co-occurrence.
Source: self-made.
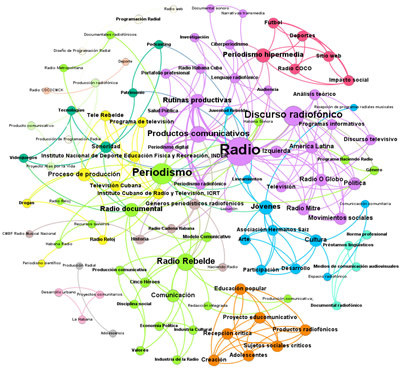
Graph 6. Keyword co-occurrence.
5. CONCLUSIONS
In the period 2013-2018, research about radio had a discreet rise in the Faculty of Social Communication of the University of Havana, highlighting the career of Journalism. Academic studies must increase their interest in the radio medium, as this will allow different views of this communication medium and its updating, for example, on issues such as information and communication technologies.
The researched topics are mainly focused on the informational area, which indicates that there is no diversity in the study of programming. There is also no variety in the tutors who guide the thesis and the collaboration between them, so both aspects should be part of the strategic lines on which the institution's work should focus.
The results indicate that it is necessary to intentionally work to awaken the motivation and interest of the students in the research of the radio medium, as well as the definition of topics that address less explored areas of radio work and the collaboration between teachers from the academy and media specialists to combine theoretical and practical experience, even when there are professors with such expertise in the faculty.
These results have outlined a line of work aimed at systematizing this type of study in the period from 2000 to the present and thus broadening and deepening the evaluation of the behavior of research regarding radio. For this, the research process is already organized from the work practices of two 2nd year Social Communication students and the 5th year diploma works of this same career.
It is expected to have a boost in the study of this media since in May of this year a new edition of the Master in Communication Sciences begins and the Communication Science Mention is made up of radio professionals who have oriented their research project towards the media.
6. REFERENCES
AUTHORS:
Beatriz Elena Fonseca Muñoz
Jefa de la Disciplina Comunicación sonora y lenguajes mediáticos. Profesora Titular. Asesora y escritora de programas dramatizados radiales. Miembro del Consejo Técnico Asesor del Centro de Estudios de la Radio y la Televisión. Profesora de la Maestría en Ciencias de la Comunicación de las provincias Camagüey y Sancti Spíritus, respectivamente. Participa como colaboradora en el Proyecto de investigación Campo de la Comunicación, que recibió el Premio de la Academia de Ciencias de Cuba en el 2018. Ha impartido cursos en diplomados y maestrías en Venezuela. Miembro del claustro de la carrera Comunicación Social en la República de Angola.
beatrizelena@fcom.uh.cu
Orcid ID: https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3100-1386
ResearchGate: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Beatriz_Fonseca8
Academia.edu: https://independent.academia.edu/BeatrizFonseca4
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/beatriz-elena-fonseca-mu%C3%B1oz-8791a7176/
Reinaldo Joel Martínez de Armas
Licenciado en Información Científico-Técnica y Bibliotecología, Universidad de La Habana. Profesor Asistente. Ha cursado pasantía en el Centro Argentino de Información Científica y Tecnológica (CAICYT). Participa como colaborador en el Programa integral de envejecimiento digno, saludable y activo en el municipio Plaza de la Revolución. Miembro del claustro la Carrera Ciencias de la Información en la República de Angola. Cursa la Maestría de Comunicación Social en la Facultad de Comunicación.
joel@fcom.uh.cu
Orcid ID: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0231-8808